Warum ist die B-DNA rechtsgängig?
Ich habe nie wirklich verstanden, warum eine DNA grundsätzlich einen Drehsinn hat und was dieser tatsächlich für die Struktur bedeutet. Wieso ist die B-DNA rechtsgängig und die Z-DNA zum Beispiel nicht?
1 Antwort
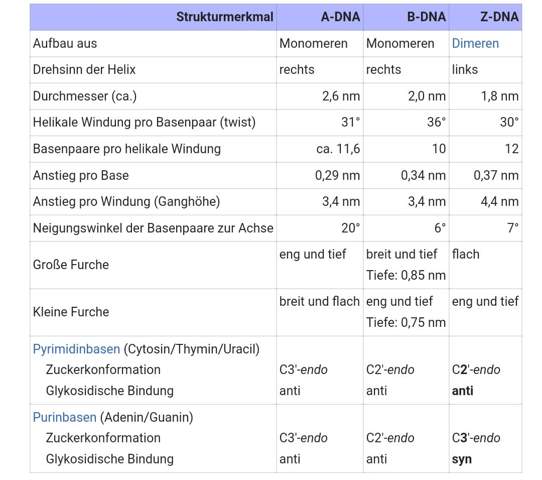
Der Drehsinn der DNA resultiert aus ihrer Struktur. Dabei ist vor allem zu bemerken, dass der größte Unterschied zwischen der B- und Z-DNA die Glykosidische Bindung der Purin- und Pyrimidinbasen ist. Bei der B-DNA liegt die der Purinbasen Adenin und Guanin in C2'-endo anti vor, während die Zuckerkonformation der Purine in der Z-DNA in C3'-endo syn vorliegt. Die A-DNA unterscheidet sich hier ebenfalls mit einer Zuckerkonformation in C3'-endo anti. Die Zuckerkonformation der Pyrimidine der B- und Z-DNA unterscheiden sich jedoch nur von der A-DNA. Zudem sind A- und B-DNA aus Monomeren aufgebaut, während die Z-DNA aus Dimeren besteht. Es liegen noch weitere Unterschiede vor:
Quelle: https://de.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Desoxyribonukleins%C3%A4ure
Zusammenfassend resultieren daraus völlig unterschiedliche Strukturen:
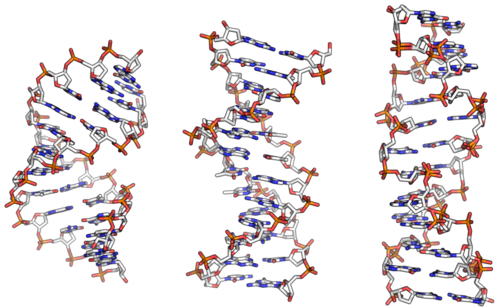
A-, B- und Z-DNA: Strukturmodelle mit jeweils 12 Basenpaaren (v. l. n. r.). Quelle: https://de.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Desoxyribonukleins%C3%A4ure
Warum die DNA überhaupt einen Drehsinn hat, sollte beim Lesen dieses Artikels klarer sein:
Why Is DNA Twisted?
DNA is coiled into chromosomes and tightly packed in the nucleus of our cells. The twisting aspect of DNA is a result of interactions between the molecules that make up DNA and water. The nitrogenous bases that comprise the steps of the twisted staircase are held together by hydrogen bonds. Adenine is bonded with thymine (A-T) and guanine pairs with cytosine (G-C). These nitrogenous bases are hydrophobic, meaning that they lack an affinity for water. Since the cell cytoplasm and cytosol contain water-based liquids, the nitrogenous bases want to avoid contact with cell fluids. The sugar and phosphate molecules that form the sugar-phosphate backbone of the molecule are hydrophilic, which means they are water-loving and have an affinity for water.
DNA is arranged such that the phosphate and the sugar backbone are on the outside and in contact with fluid, while the nitrogenous bases are in the inner portion of the molecule. In order to further prevent the nitrogenous bases from coming into contact with cell fluid, the molecule twists to reduce space between the nitrogenous bases and the phosphate and sugar strands. The fact that the two DNA strands that form the double helix are anti-parallel helps to twist the molecule as well. Anti-parallel means that the DNA strands run in opposite directions, ensuring that the strands fit tightly together
This reduces the potential for fluid to seep between the bases.
Quelle: https://www.thoughtco.com/double-helix-373302